If you’ve recently acquired a new car, it’s not only a happy moment for you and your family, but it’s also a happy occasion for the government, as they’ll be collecting numerous taxes from the vehicle you’ve just purchased. In this post, we’ll look at why automobiles are so expensive in India, and how taxes play a big part in that.
Why cars are so expensive in india as compared to US or other nations?
1. GST Rates on Cars
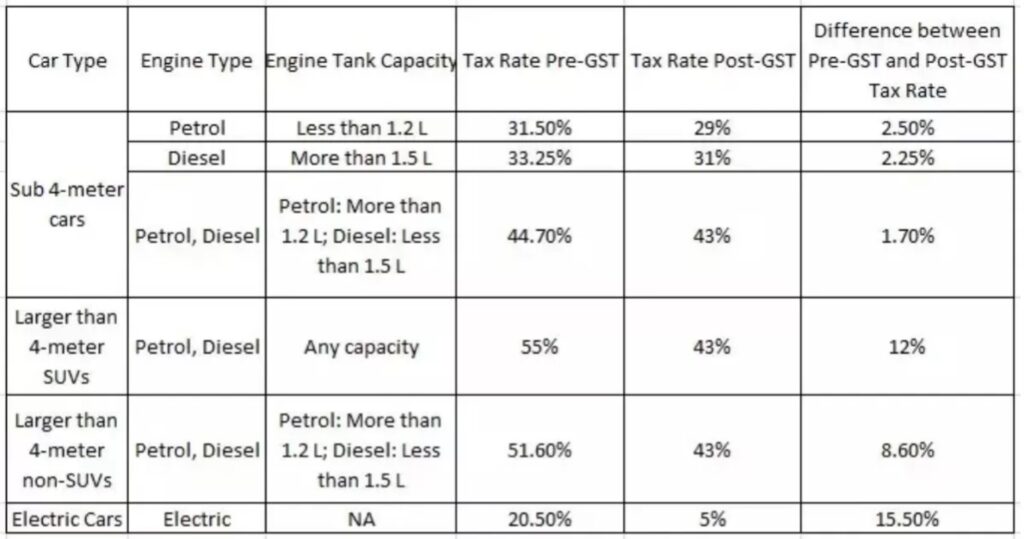
GST rates range from 29 percent to nearly 50 percent, depending on the automobile and engine. Vehicles with a petrol engine less than 1.2 litre and a length of less than four metres are subject to a combined tax of 28 percent GST and one percent CESS, for a total of 29 percent. Similarly, this fee varies each vehicle, depending on its length, fuel type, and engine size.
2. Road Tax & Registration Charges
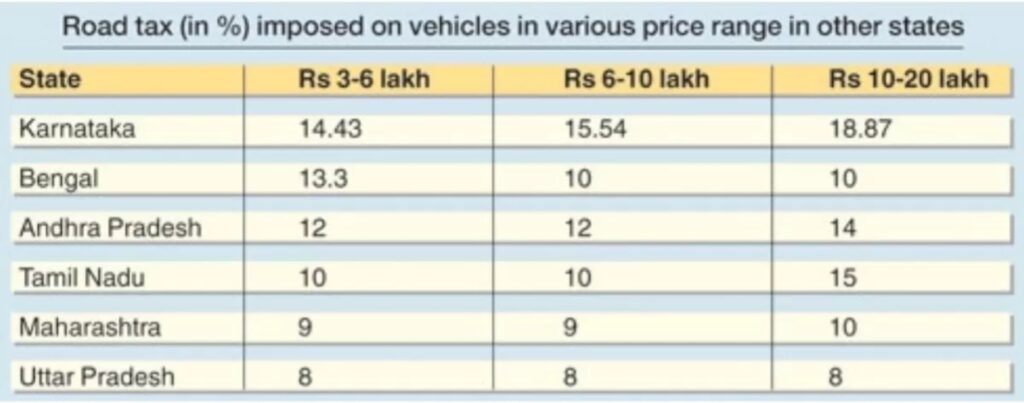
State government applies road tax and this differs from state to state depending on the type of the car, the fuel it uses and the engine capacity. Registration charges are applicable when you buy a new vehicle as well as when you buy a used vehicle.
3. Expensive cars in India – Excise Duty on Fuel
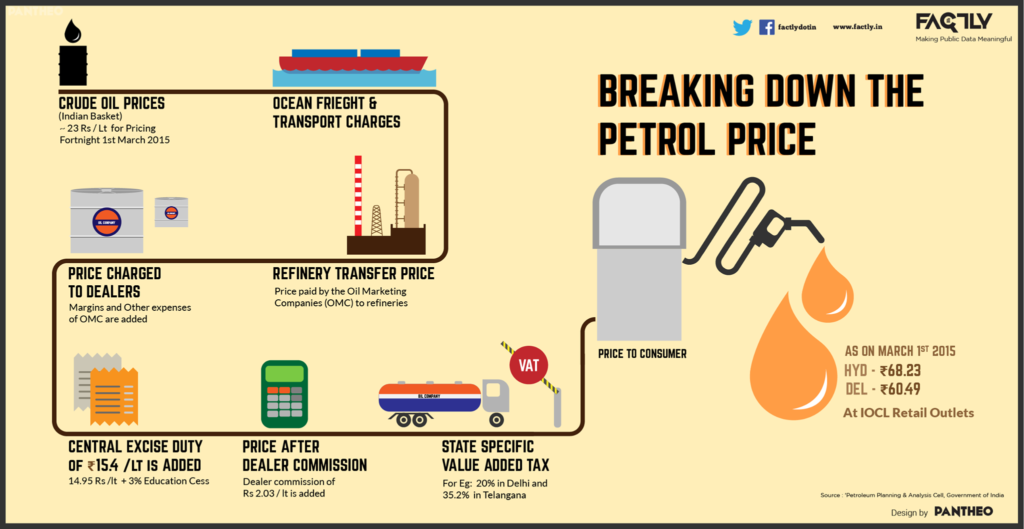
The car that you buy operates on fuel (petrol, diesel or CNG). But you pay excise duty on the fuel that you use for your car which ranges from 35 percent to 45 percent of the fuel price.
4. Other Charges and Taxes

When you renew your insurance, get your car serviced, or buy parts and accessories, you’ll have to pay 18 percent GST. Once you’ve bought an automobile, you’ll have to pay taxes.
5. Expensive cars in India – Import Duty
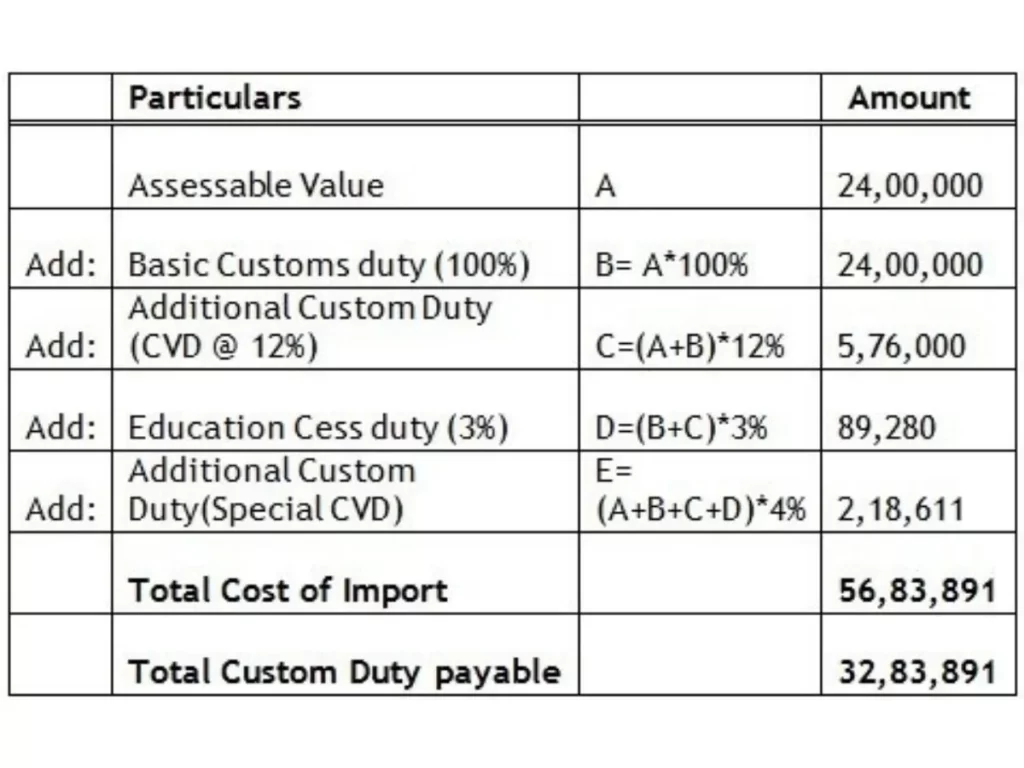
Currently, India charges a 100% duty on fully imported cars with a CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) value of more than USD 40,000 and a 60% duty on those having a CIF value of less than USD 40,000, as shown in the table above. If you buy a car for Rs 24 lakh, you will have to pay Rs 56,83,891 in import costs and another Rs 32,83,891 in customs duty, bringing the total cost of the car to Rs 1,13,67,782.
6. Cost of Parts

The car may or may not be imported as a CBU (Complete Built-Up) unit. Parts are often imported and then built in India as CKD (Complete Knock Down) units. Imported parts under the CKD system are likewise subject to high taxes. Import duty is assessed at 30% for engine or gearbox mechanisms that are pre-assembled but not mounted on a chassis or body assembly. Engines, gearboxes, and transmission mechanisms that are not pre-assembled are subject to a 10% import duty.
7. Expensive cars in India – Dealer Markup

‘Dealer Markup’ is a term that only a few individuals are familiar with. This pertains to the vehicle’s cost, margins, and pricing. The amount of markup a shopkeeper is permitted impacts how much money he makes on each unit of product sold. The more the markup, the higher the consumer’s cost and the more money the store makes. This is also a factor that contributes to the high cost of automobiles in India.


