These comfort and safety amenities were previously exclusively accessible in expensive vehicles. However, in inexpensive hatchbacks, they are currently required. Continue reading to learn more about them.
1. Power Windows

After power steering, motorised windows is the technology that has made automobile travel the most pleasant. An electric motor drives the window winder assembly in a power window, which is a basic technique. This technology became well-known a few years ago as an option in many low-end hatchbacks with only the front windows motorised. Most low-end automobiles now have all four power windows as standard equipment, while mid-range cars have all four power windows as standard equipment.
2. Airbags
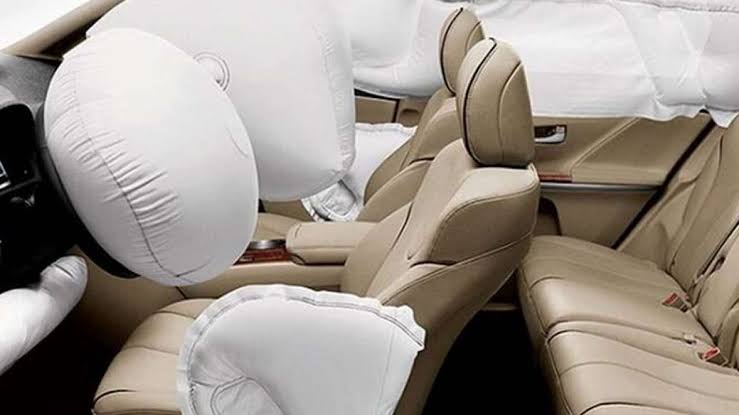

Airbags are a necessary and life-saving technical advancement. After the collision sensors detect a hit, the folded-up cloth sacks explode. This is accomplished with the aid of a very sensitive small explosive device that activates instantly after a collision. Airbags protect the driver and co-passenger from jerks or foreign objects impacting with the frontal area of the vehicle. Despite the fact that airbags are now a standard feature, they were formerly exclusively found in expensive automobiles where passenger safety was paramount. As with ABS, the RTO authorities have made airbags an obligatory equipment in automobiles starting August 2021, owing to an increase in traffic accident deaths. With the latest ruling from RTO, all four-wheelers manufactured in India after December 2021 must have dual airbags in them.
3. ABS

ABS, or Anti-lock Braking System, is a ground-breaking technology that prevents tyres from locking up during emergency braking. Mercedes Benz was the first to bring this technology to the automobile industry. ABS used to be a high-value safety feature available primarily in high-end vehicles. Though ABS was available in lower-end automobiles in recent years, it was only given as an option. Following the RTO judgement in April 2019, all car manufacturers were required to include ABS in all vehicles produced.
4. Power Mirrors
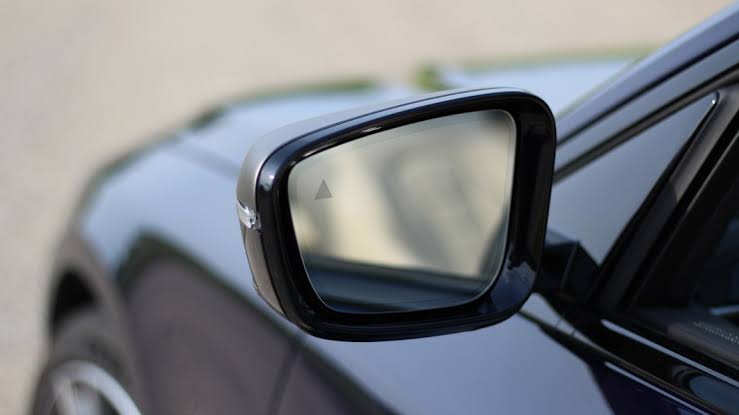

Mercedes Benz and other international automobiles were the first to introduce power mirrors to the Indian market. With power mirrors, the driver may adjust ORVMs using an electrical toggle switch in the cabin. In the early 2000s, this trend was seen in mid-size and premium automobiles. Many entry-level hatchbacks now have power mirrors, thanks to the improved availability of technology and Indian manufacturers’ efforts to keep up with global norms. Many tiny hatchbacks also allow drivers to automatically fold their ORVMs, assuring mirror safety in dangerous parking places and ease of adjustment even in bad weather.
5. Power Steering
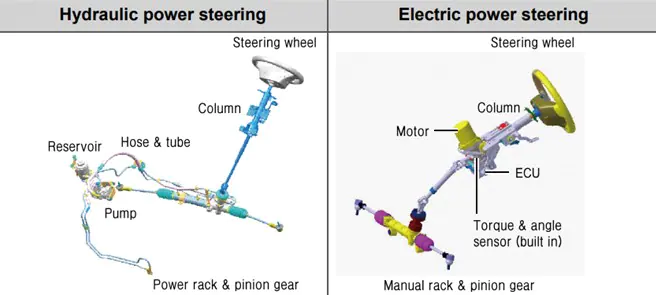
Around 20 years ago, the power steering assembly consisted of a hydraulic unit which made the use of steering fluid essential. This hydraulic pump was driven by the engine directly. Owing to the additional changes and modifications in the steering assembly, providing this option in budget cars was a costly affair. But now, electric power steering units can be attached to a typical non-power steering assembly with ease and minimal alterations. Though power steering is being adopted in nearly all cars available in the market, some manufacturers have decided to omit this option in some of their lowest budget models due to the competitive pricing and lack of dedicated regulations or guidelines for the same. (www.lambertsfruit.com)

