In the year 2014, Formula 1 saw one of the most significant changes in the history of F1 motorsports. The traditional technique of using only a standard fuel-powered single Internal combustion engine was changed. The new regulations brought in by FIA made it cleared that motorsport should start to think about a cleaner and greener step in racing. The modern F1 cars can only use 110kgs of fuel per race without refueling so here steps in the HYBRID tech.
The naturally aspirated 2.4-liter V8 engines were replaced with new, 1.6-liter turbocharged V6 Engines. Teams are no more calling them ENGINES instead they are referred to as “POWER UNITS“

COURTSEY- MOTORSPORT TECHNOLOGY
Components of Power Units
These F1 hybrid power units are comprised of 6 major parts, those are –
1. ICE (Internal Combustion Engine)
2. TC (Turbocharger)
3. MGU-K (Motor generation unit – Kinetic)
4. MGU-H (Motor generation unit – Heat)
5. ES (Energy store)
6. CE (Control electronics or ECU)
The recent Formula 1 2020 season witnessed four power units which were – Mercedes AMG High-Performance Powertrains (Constructors Championship winner), Honda, Ferrari, and Renault Sport.
1. Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
Every engine is a powerhouse of a car. All of these huge power units built around 4-stroke 1600cc, 6 cylinders, direct injection engines. The engines equipped with a single hybrid turbocharger. These engines are smaller and much lighter however have the capacity to produce a maximum power output of 1,160HP @10,500 rpm. All these F1 engines are way more efficient than other regular road engines. The engine is in the V6 configuration with a 90° cylinder angle. The maximum bore and stroke are 80mm and 53mm respectively. It uses a 24 valves DOHC valvetrain having 4 valves/cylinder. The maximum achievable revs of the engine are 15,000 rpm and can give an approximated torque of 650 N-m.
2. Turbocharger (TC)
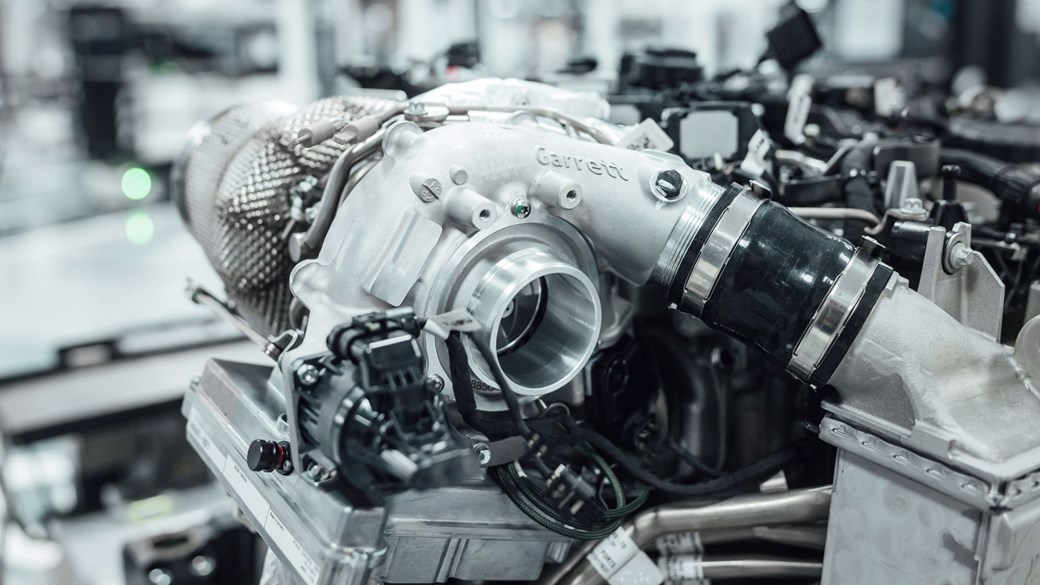
Mercedes AMG-HPP(Garrett Motion Turbos)
A turbocharger or a turbo is a component used to boost the power output of the Engine. The objective of TC is to increase the volumetric efficiency of the engine by increasing the density of intake charge resulting allowing more power per cycle. A turbocharger uses the energy from the exhaust gas to increase the density of the intake air going inside the engine cylinder and therefore resulting in more power. It allows smaller engines to produce more output in the same set of conditions without changing the engine size. An F1 turbo is used to drive the compressor and also the waste heat energy then powers the MGU-H. F1 turbo is capable of a 125,000 spin rev limit and weighs about 8 kg depending upon external housing.
3. MGU-K (Motor generation unit – Kinetic)
The MGU-K is one of the most complex and vital devices in modern Formula racing. It is like a generator. MGU-K can be located directly near the crankshaft of the engine. It captures the energy generated by moving car under braking conditions. Kinetic energy is stored in the form of electrical in energy storage . When the driver feels the need for more power or to overtake the car in front he could deploy this stored energy back to MGU-K which will eventually supply more power to the crank of the engine. MGU-K can take power from the energy store or MGU-H depending on the situation.
Driver when in need can control ERS (energy regenerative system). It can generate up to 160 Bhp of the drive.
4. MGU-H (Motor generation unit – Heat)
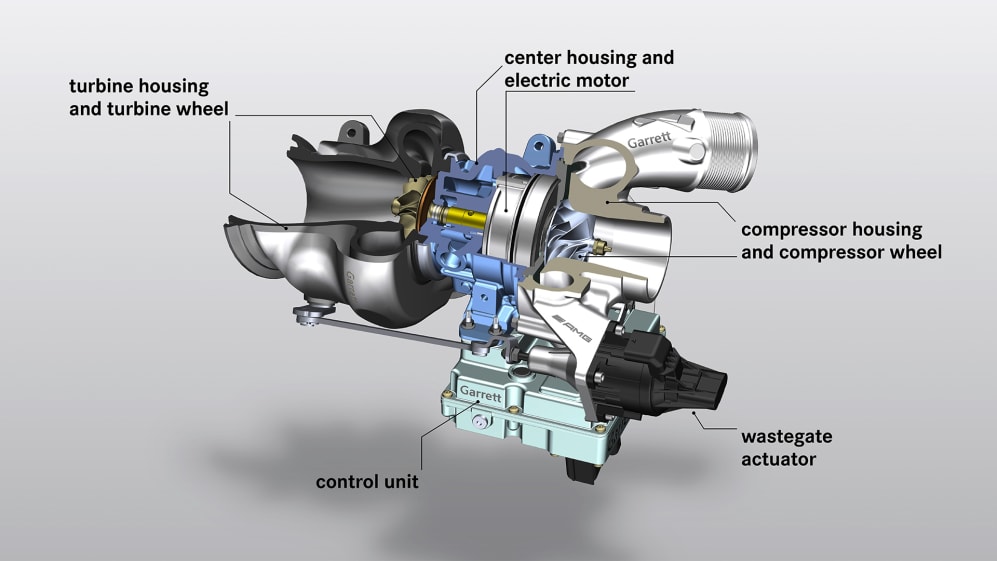
Image courtesy- Mercedes motorsports F1
The MGU-H is coupled with the Turbocharger(TC). It can also act as a generator unit by sucking the energy from the exhaust gases used to spin the turbine of the turbocharger in an F1 car. This energy is then sent to battery store in electrical form. It can also redirect power to MGU-K instantly while working without reserving energy in storage. it can also serve the purpose to control the speed of Turbo by sending the required power IN or OUT of the turbo. The recovered energy from exhaust is absorbed by MGU-H and converted into electrical energy, which drives the turbocharger. This results in the elimination of Turbo-Lag.
5. ES (Energy store)
Energy store can be considered as a Big battery unit. Both heat energy and kinetic energy are taken from MGU-H & MGU-K respectively are stored in the Energy store. When the car is in motion and the driver is not in need of an external boost or power, then all the energy gets redirected towards the energy store. The driver can engage in recharge mode when not in use.
6. CE (Control electronics or ECU)

The Control electronics acts as an ECU in a car which monitors all the functions and provides desirable output performance to the driver when drivers give any kind of input, like altering the differential settings, changing fuel mix, engaging various modes while overtaking, enabling ERS, and much more. Control electronics also ensures the conversion of collected energy form before storage. It is a linking medium between the MGU and Energy storage in simple terms.

